E-governance, or electronic governance, means using Information and Communication Technology in government work. It makes things clear, responsible, and fast. This helps services be fair and easy to use. Now, in our digital age, e-governance is not just for being modern but is key for the growing the country
E-governance has become an important aspect of how governments run and communicate over the last few years. It has changed the manner in which governments operate and interact with their citizens, becoming easier and more efficient.
How E-Governance Works
E-governance means that citizens can access all government services through digital platforms such as websites, mobile apps, and online portals. Citizens can access government services, pay, submit documents, and receive updates. A citizen can now pay their taxes, renew their licenses or apply for permits from their homes and hence do not need to walk into government offices. It has reduced the waiting times and improved the delivery of services.
Why E-Governance is Important
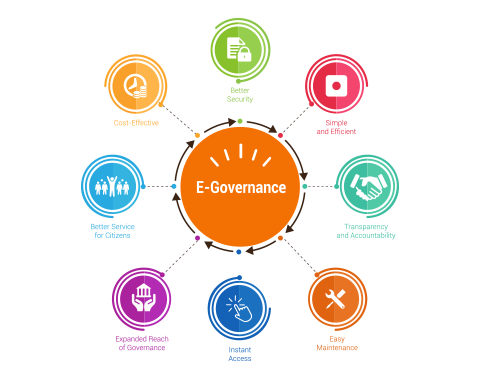
Improved Access and Accessibility
E-governance helps in making government services reachable to all. This can be done even if the person is located in a remote area or has a busy schedule since he or she can have access to the services even from home or on-the-go.This has been very helpful during the pandemic when in-person visits to government offices were limited.
Transparency and Accountability
Digital platforms enable citizens to trace the progress of their applications and how funds are utilized by the government. The transparency builds up trust between the government and its people, which means it will be easier to account for any official’s deeds.
Cost and Time Efficiency
By moving services online, governments can save on operational costs, such as office space and paperwork. Citizens also benefit from the reduction in time spent in long queues or waiting for manual processing. This leads to a more efficient and effective system for both parties.
Boosting Citizen Participation
E-governance enables participation in decision-making actively through online surveys, digital feedback forms, and electronic town halls through which citizens can comment upon and contribute to policies relevant to them. This facilitates greater inclusive governance.
Competitive Positioning Globally
A country that embraces more pervasive e-governance stands better positioned in competing internationally. The efficient governmental working enables business attraction along with investment, hence enabling all-round development of the nation as a whole.
What is E-governance?

E-governance is one of the most cutting-edge efforts to develop effective governance. Currently, practically all developed, undeveloped, and developing nations use e-governance aspects to aid in their national growth.
Thus, its significance in the modern world is enormous. The solutions to all the queries about e-governance are provided below. By integrating ICT (Information and communications technology) into the governance processes, a new paradigm known as “Electronic-Governance” or “E-Government” has emerged in the field of governance.
In terms of dependable access to information within government, between government, at the national, state, municipal, and local level, among citizens, and businesses, e-governance improves transparency, accountability, efficiency, and effectiveness of the governing process.
It also empowers businesses through information access and use. Giving citizens access to transparent, egalitarian, and accountable service delivery is the main goal of electronic government. The goal of e-governance is to ensure that people participate in the political process through electronic channels like email, websites, SMS connectivity, and others while facilitating and improving the quality of governance.
E-governance keeps the government in step with fast changes in the digital world. This helps solve modern problems like handling data, using resources wisely, and keeping people involved.
Types of E-Governance
E-governance can be divided into the following types, each serving different needs:
- Government-to-Citizen (G2C): Helps people get public services like paying taxes online and document requests
- Government-to-Business (G2B): G2B helps the government and companies work together for better bids and licenses.
- Government-to-Government (G2G): G2G aids in sharing info and working together among different government departments.
- Government-to-Employee (G2E): G2E supports the government in managing workers and internal communication.
Each type of electronic governance helps address distinct challenges and opportunities such that benefits from digital transformation are diffused among all sectors. For example, G2C initiatives might help fill the gap between rural and urban communities by providing equal accessibility to vital services.
SMART Governance Explained
ICTs for SMART Governance
The tremendous potential of the government to serve the people is realized through its practical application and use of ICT to provide efficient and affordable services, information, and knowledge to the citizens being governed. It established connections between the state and society, government and people, human interaction, and governance. It will alter how people interact with the government in the same ways that it alters how people interact with one another.
SMART Governance : With the use of ICTs, we are able to achieve smart governance as discussed in below mentioned points.
- S(Simple): Means avoiding complex procedures and simplifying government rules and regulations, resulting in a more user-friendly administration.
- M(Moral): It refers to the introduction of a new system into the political and administrative structures along with technological advancements to increase the effectiveness of various government institutions.
- A(Accountable): Ensure that public service employees are held accountable by creating efficient information management systems and other performance monitoring tools.
- R(Responsive): Process streamlining speeds up the system’s response time, making it more responsive.
- T(Transparent): Providing information in the public domain, such as via websites or other portals, makes government functions and processes transparent.
The SMART governance principles are consistent with the overall global goals of sustainability. These comprise responsible resource use, inclusivity, and proper ethics. For instance, in applying green ICT practices in service delivery, a government can lessen its carbon footprint.
What connection does ICT have with governance?
Governmental procedures are improved using ICT in public administrations, which also ensures sustained development. The use of ICT in all facets of governance can eliminate pointless human engagement in the delivery of services from the state to its constituents. So, through enhancing transparency and accountability in the public sectors, ICT has been fostering good governance. It promotes decision-making, public involvement, and the effective delivery of products and services to the populace. The procedure of ensuring the citizen’s right to information and functions was developed in this context using ICT. Through their websites or e-platforms, government institutions and sectors have been informing the public about their accomplishments, programs, and plans. Additionally, residents can use the to provide comments or ask questions about any initiatives or programs that most directly affect them from their homes.
In fact, integrating ICT reduces the costs associated with the administration and hastens service delivery. The utilization of blockchain technology can therefore ensure integrity and security for public records, thus developing confidence between citizens.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of E-Governance
- Estonia: Often referred to as the “e-Government Pioneer,” Estonia’s comprehensive digital transformation allows citizens to vote online, access healthcare records, and manage taxes digitally.
- India: The Aadhaar initiative, the world’s largest biometric system, has streamlined identity verification, enabling efficient delivery of subsidies and benefits.
- Singapore: Known for its Smart Nation program, Singapore uses ICT to optimize urban planning and public service delivery.
These examples outline the transformative power of e-governance in bringing in inclusive and efficient societies. Estonia’s success exemplifies how small nations can be the leader in innovation, and India’s scale exemplifies that such implementation can be viable in large numbers.
Comparing Traditional and SMART Governance
Traditional governance uses manual steps. This can lead to slowdowns and problem. For example, Manual tax filing requiring physical visits to government offices. In case of SMART Governance: Online tax portals enabling quick, transparent, and user-friendly processes.
Moving from old to SMART governance is a big change. It needs training for officials and people. This way, everyone gets ready and can use the new system well. This shift is not just better, it changes how the government and people work together for the better.
Merits and Demerits of electronic governance
Now, let’s discuss the main advantages and disadvantages of e-governance. The ability to offer residents a wider range of governmental services in a methodical and economical manner is the goal of e-governance. Because it enables the public to learn about the government’s projects and the policies it is attempting to enact, it promotes government openness. Enhancing the effectiveness of the current system will be the key benefit of implementing electronic government. Another benefit is that it strengthens interactions between the public and civic authorities, lowers costs, boosts revenue growth, and increases transparency in the administration. The primary drawback of e-governance is the lack of impartial public internet access, reliable online information, and covert government group agendas that could influence and sway public opinion.
To solve the challenges mentioned, a multi-stakeholder approach is necessary. The government needs to engage with private sectors and civil society in building resilient and inclusive digital ecosystems.
Best Practices for Implementing E-Governance
To ensure successful implementation, governments must:
- Build Robust Digital Infrastructure: Invest in high-speed internet and secure data storage systems.
- Promote Digital Literacy: Educate citizens and employees about using e-governance tools.
- Ensure Data Privacy: Establish strong cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information.
Other strategies include the adoption of open-source technologies to reduce costs and encourage innovation. Feedback mechanisms can also be established to ensure continuous improvement of e-governance systems by governments.
How E-Governance Transforms Key Sectors
E-governance is changing the nature of many sectors, which are becoming more efficient, accessible, and service delivery-oriented.
Healthcare
How does e-governance transform public health administration? E-governance in healthcare enhances with EHRs, where all patient data is organized for better diagnosis and treatment. Telemedicine also makes it possible to reach remote areas. AI tools also help in disease surveillance and health trend prediction.
Courses like MBA in Healthcare management focuses on Healthcare e-governance systems and management
Education
Digital platforms encourage e-learning and make education more accessible. Smart classrooms bridge the gap between urban and rural divisions, while VR technology enriches learning experiences through its immersion. E-governance also makes administrative tasks simpler by online registration and payment of fees.
Public Administration
E-governance automates the administrative process, which has made government services much more efficient. Services like the application for a birth certificate are now available online, reducing waiting time and increasing accessibility. Automation increases transparency and reduces human error.
Conclusion
It is clear from the examination of e-meaning, government’s objectives and features that e-government plays a key role in today’s period of globalization. This is advantageous, especially for developing nations. All these nations have been able to maintain their development trends on par with the industrialized nations because of the introduction of e-governance. The power of knowledge. By providing pertinent information with the least amount of effort, expense, and expense, e-governance empowers us.
The future of e-governance depends on using new tech like AI, IoT, and blockchain to make strong and flexible systems. As we go more digital , the principles of e-governance will play a crucial role in shaping equitable and sustainable futures.
Connecting E-Governance to Professional Development E-governance is not just about governance; it also opens pathways for professionals to specialize in this growing field. Westford Uni Online offers several courses that is closely related to e-governance like MBA in Cyber Governance and Digital Transformation which focus on the intersection of governance, technology, and leadership.
About Westford Uni Online
Westford Uni Online is a synchronous learning platform with transnational higher education partners. In its efforts to expand the horizons of learning and growth for its pupils, this blended learning platform offers undergraduate and postgraduate degree programs in unique and upcoming fields such as MBA in Global Business Administration with Cyber Governance and Digital Transformation that enables professionals to specialize within cyber governance, digital transformation and global business administration. This programme caters to those who look forward to growing in government or legal sectors and wish to further build upon their knowledge of the digitalization for the purpose of personal and professional growth.
E-Governance FAQ
E-governance, or electronic governance, is the technology of applying ICT (Information, Communication, and Technology) to improve governance. Not only can citizens access and benefit from government services, but businesses can also gain from the advancements of e-governance. It aims for the betterment of transparency, communication, and potency between
- Government and citizens (G2C),
- Government and business (G2B),
- Government-and-Government (G2G), and
- Government and employees (G2E).
Yes, there are specialized programs focusing on e-governance and law. At Westford Uni Online, you can find the best courses and programs that integrate e-governance and law. MBA in Cyber Governance and Digital Transformation combines governance and automation, and MBA in Global Business Administration with Cyber Governance and Digital Transformation, which helps professionals and students to excel in e-governance and global business administration.
References:
- What is E-Governance: Meaning, Objectives & Features
- E-Governance – GeeksforGeeks
- Dwivedi and Bharti (2005): ‘E-Governance in India- Problems and Acceptability’, Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, New Delhi, Pp. 37-42.
- Kumar, P and Kumar, D &et al. (2013). ICT in Local Self Governance: A study of Rural India. International Journal of Computer Applications. Retrieved February 23, 2018, from ICT in Local Self Governance: A Study of Rural India.
- Katyal, N. (2002). “The white box revolution”. Data Quest, Special Issue Vol.XX, No: 14, July 31, 2002, pp.II-IV.





